Melody
Generally for modern styles of music, melodies follow the chord progression.In Practical Terms
Generally, melodies:- Use chord tones on chord changes
- Use repeated / recursive structures
Example chord progression:
-

C | Em | Dm | G
A simple melody could be:
-

Notes E | G | F | D
(from chord tones)
Melody overlaid with chord progression:
-

C | Em | Dm | G
Add more notes and rhythms to the line for more interest.
Melodies use repeated / recursive structures. Repetition is either verbatim, or repeated at different pitches, or repeated with other variation. Example:
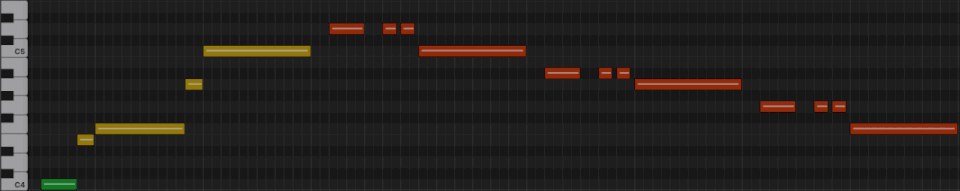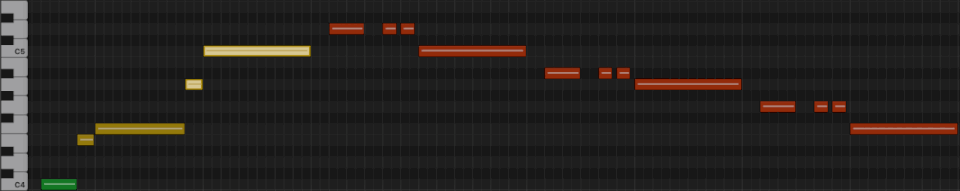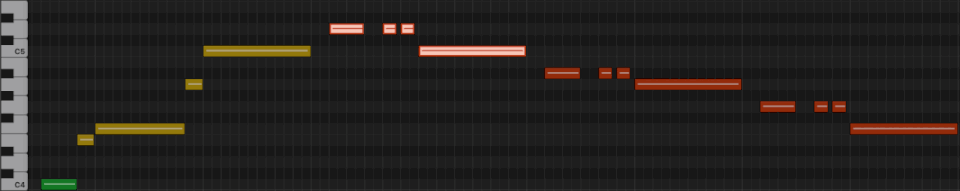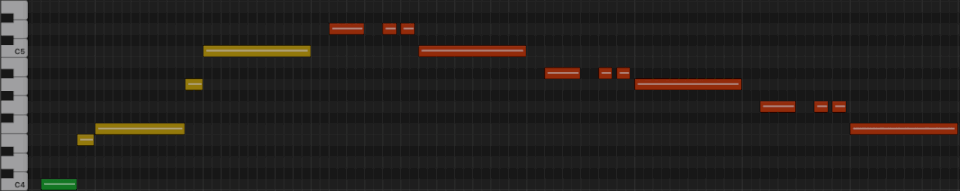
First line from "What a Wonderful World"

Repetition of the greater structure
Musical structures are often recursive / nested / fractal-like.
More Info
Many styles of melodies exist, but generally they work on the wider principles of tension followed by resolution, and repeated structures.Tension can be created by:
- Using non-chord tones
- Using notes outside of the key
- Increasing pitch
- Rhythmic syncopation
Tension can be resolved by:
- Resolving to chord tones
- Resolving to notes within the key
- Decreasing pitch
- Resolving syncopation (landing on a strong beat)
Repetition can be found at every scale (i.e., when you zoom in / zoom out) in music, from the smallest rhythmic / melodic unit to entire sections of the music.